Spaces:
Sleeping
Sleeping
File size: 11,904 Bytes
7370e5c |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 |
---
comments: true
description: Master instance segmentation and tracking with Ultralytics YOLOv8. Learn techniques for precise object identification and tracking.
keywords: instance segmentation, tracking, YOLOv8, Ultralytics, object detection, machine learning, computer vision, python
---
# Instance Segmentation and Tracking using Ultralytics YOLOv8 🚀
## What is Instance Segmentation?
[Ultralytics YOLOv8](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/) instance segmentation involves identifying and outlining individual objects in an image, providing a detailed understanding of spatial distribution. Unlike semantic segmentation, it uniquely labels and precisely delineates each object, crucial for tasks like object detection and medical imaging.
There are two types of instance segmentation tracking available in the Ultralytics package:
- **Instance Segmentation with Class Objects:** Each class object is assigned a unique color for clear visual separation.
- **Instance Segmentation with Object Tracks:** Every track is represented by a distinct color, facilitating easy identification and tracking.
<p align="center">
<br>
<iframe loading="lazy" width="720" height="405" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/75G_S1Ngji8"
title="YouTube video player" frameborder="0"
allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share"
allowfullscreen>
</iframe>
<br>
<strong>Watch:</strong> Instance Segmentation with Object Tracking using Ultralytics YOLOv8
</p>
## Samples
| Instance Segmentation | Instance Segmentation + Object Tracking |
| :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
| 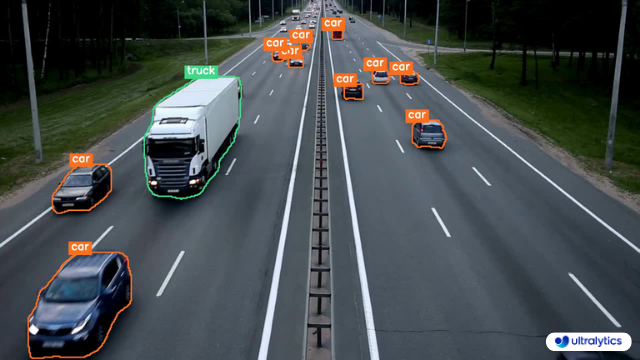 | 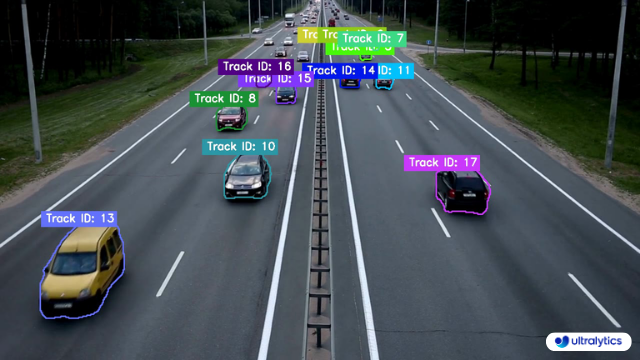 |
| Ultralytics Instance Segmentation 😍 | Ultralytics Instance Segmentation with Object Tracking 🔥 |
!!! Example "Instance Segmentation and Tracking"
=== "Instance Segmentation"
```python
import cv2
from ultralytics import YOLO
from ultralytics.utils.plotting import Annotator, colors
model = YOLO("yolov8n-seg.pt") # segmentation model
names = model.model.names
cap = cv2.VideoCapture("path/to/video/file.mp4")
w, h, fps = (int(cap.get(x)) for x in (cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH, cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT, cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS))
out = cv2.VideoWriter("instance-segmentation.avi", cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*"MJPG"), fps, (w, h))
while True:
ret, im0 = cap.read()
if not ret:
print("Video frame is empty or video processing has been successfully completed.")
break
results = model.predict(im0)
annotator = Annotator(im0, line_width=2)
if results[0].masks is not None:
clss = results[0].boxes.cls.cpu().tolist()
masks = results[0].masks.xy
for mask, cls in zip(masks, clss):
color = colors(int(cls), True)
txt_color = annotator.get_txt_color(color)
annotator.seg_bbox(mask=mask, mask_color=color, label=names[int(cls)], txt_color=txt_color)
out.write(im0)
cv2.imshow("instance-segmentation", im0)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord("q"):
break
out.release()
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
```
=== "Instance Segmentation with Object Tracking"
```python
from collections import defaultdict
import cv2
from ultralytics import YOLO
from ultralytics.utils.plotting import Annotator, colors
track_history = defaultdict(lambda: [])
model = YOLO("yolov8n-seg.pt") # segmentation model
cap = cv2.VideoCapture("path/to/video/file.mp4")
w, h, fps = (int(cap.get(x)) for x in (cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH, cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT, cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS))
out = cv2.VideoWriter("instance-segmentation-object-tracking.avi", cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*"MJPG"), fps, (w, h))
while True:
ret, im0 = cap.read()
if not ret:
print("Video frame is empty or video processing has been successfully completed.")
break
annotator = Annotator(im0, line_width=2)
results = model.track(im0, persist=True)
if results[0].boxes.id is not None and results[0].masks is not None:
masks = results[0].masks.xy
track_ids = results[0].boxes.id.int().cpu().tolist()
for mask, track_id in zip(masks, track_ids):
color = colors(int(track_id), True)
txt_color = annotator.get_txt_color(color)
annotator.seg_bbox(mask=mask, mask_color=color, label=str(track_id), txt_color=txt_color)
out.write(im0)
cv2.imshow("instance-segmentation-object-tracking", im0)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord("q"):
break
out.release()
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
```
### `seg_bbox` Arguments
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
| ------------ | ------- | --------------- | -------------------------------------------- |
| `mask` | `array` | `None` | Segmentation mask coordinates |
| `mask_color` | `RGB` | `(255, 0, 255)` | Mask color for every segmented box |
| `label` | `str` | `None` | Label for segmented object |
| `txt_color` | `RGB` | `None` | Label color for segmented and tracked object |
## Note
For any inquiries, feel free to post your questions in the [Ultralytics Issue Section](https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics/issues/new/choose) or the discussion section mentioned below.
## FAQ
### How do I perform instance segmentation using Ultralytics YOLOv8?
To perform instance segmentation using Ultralytics YOLOv8, initialize the YOLO model with a segmentation version of YOLOv8 and process video frames through it. Here's a simplified code example:
!!! Example
=== "Python"
```python
import cv2
from ultralytics import YOLO
from ultralytics.utils.plotting import Annotator, colors
model = YOLO("yolov8n-seg.pt") # segmentation model
cap = cv2.VideoCapture("path/to/video/file.mp4")
w, h, fps = (int(cap.get(x)) for x in (cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH, cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT, cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS))
out = cv2.VideoWriter("instance-segmentation.avi", cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*"MJPG"), fps, (w, h))
while True:
ret, im0 = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
results = model.predict(im0)
annotator = Annotator(im0, line_width=2)
if results[0].masks is not None:
clss = results[0].boxes.cls.cpu().tolist()
masks = results[0].masks.xy
for mask, cls in zip(masks, clss):
annotator.seg_bbox(mask=mask, mask_color=colors(int(cls), True), det_label=model.model.names[int(cls)])
out.write(im0)
cv2.imshow("instance-segmentation", im0)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord("q"):
break
out.release()
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
```
Learn more about instance segmentation in the [Ultralytics YOLOv8 guide](#what-is-instance-segmentation).
### What is the difference between instance segmentation and object tracking in Ultralytics YOLOv8?
Instance segmentation identifies and outlines individual objects within an image, giving each object a unique label and mask. Object tracking extends this by assigning consistent labels to objects across video frames, facilitating continuous tracking of the same objects over time. Learn more about the distinctions in the [Ultralytics YOLOv8 documentation](#samples).
### Why should I use Ultralytics YOLOv8 for instance segmentation and tracking over other models like Mask R-CNN or Faster R-CNN?
Ultralytics YOLOv8 offers real-time performance, superior accuracy, and ease of use compared to other models like Mask R-CNN or Faster R-CNN. YOLOv8 provides a seamless integration with Ultralytics HUB, allowing users to manage models, datasets, and training pipelines efficiently. Discover more about the benefits of YOLOv8 in the [Ultralytics blog](https://www.ultralytics.com/blog/introducing-ultralytics-yolov8).
### How can I implement object tracking using Ultralytics YOLOv8?
To implement object tracking, use the `model.track` method and ensure that each object's ID is consistently assigned across frames. Below is a simple example:
!!! Example
=== "Python"
```python
from collections import defaultdict
import cv2
from ultralytics import YOLO
from ultralytics.utils.plotting import Annotator, colors
track_history = defaultdict(lambda: [])
model = YOLO("yolov8n-seg.pt") # segmentation model
cap = cv2.VideoCapture("path/to/video/file.mp4")
w, h, fps = (int(cap.get(x)) for x in (cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH, cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT, cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS))
out = cv2.VideoWriter("instance-segmentation-object-tracking.avi", cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*"MJPG"), fps, (w, h))
while True:
ret, im0 = cap.read()
if not ret:
break
annotator = Annotator(im0, line_width=2)
results = model.track(im0, persist=True)
if results[0].boxes.id is not None and results[0].masks is not None:
masks = results[0].masks.xy
track_ids = results[0].boxes.id.int().cpu().tolist()
for mask, track_id in zip(masks, track_ids):
annotator.seg_bbox(mask=mask, mask_color=colors(track_id, True), track_label=str(track_id))
out.write(im0)
cv2.imshow("instance-segmentation-object-tracking", im0)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord("q"):
break
out.release()
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
```
Find more in the [Instance Segmentation and Tracking section](#samples).
### Are there any datasets provided by Ultralytics suitable for training YOLOv8 models for instance segmentation and tracking?
Yes, Ultralytics offers several datasets suitable for training YOLOv8 models, including segmentation and tracking datasets. Dataset examples, structures, and instructions for use can be found in the [Ultralytics Datasets documentation](https://docs.ultralytics.com/datasets/).
|